Science
Deadly Airborne Fungus Aspergillus Spreads Rapidly Across Five U.s. States, Scientists Warn
These days, it feels like negative news is always present when you visit a website or pick up a newspaper. A dangerous airborne virus that can eat away at your flesh from the inside out has now prompted warnings in five major US states.
If the missile exchange between Israel and Iran as Russia teeters on the verge of World War III isn’t enough, we also fear that artificial intelligence will exterminate humanity. What about harbinger asteroids speeding towards Earth? The Doomsday Clock is getting closer to midnight than ever before, which is not surprising, yet it feels like a scene from The Last of Us has come to life. The computer game Naughty Dog and the live-action version on HBO depict a destroyed Earth following the transformation of humanity into mushroom monsters by the real-life Cordyceps fungus. According to scientists, we should be on the lookout for Aspergillus fumigatus instead than Cordyceps because the latter hasn’t yet made a proper leap to humans. It is nearly impossible to avoid this airborne fungus, as humans can inhale microscopic spores without realising it. As temperatures rise, there are concerns that Aspergillus fumigatus will continue to spread, putting hundreds of thousands of people at risk of developing aspergillosis, a dangerous lung illness. Aspergillosis can cause organ failure and even death in susceptible people.
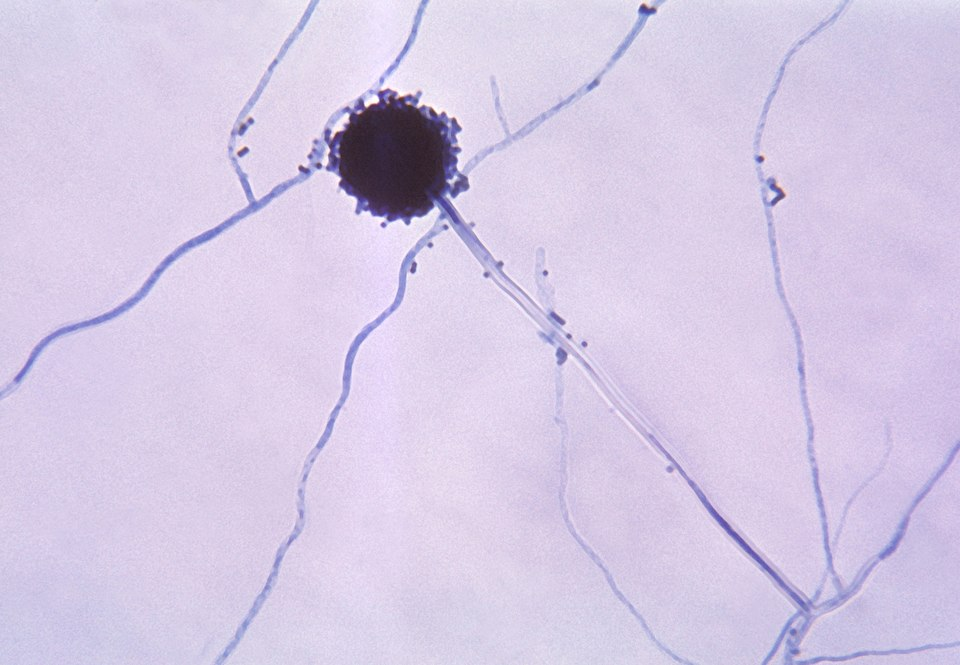
Aflatoxin, one of the most potent naturally occurring carcinogens in the world, is produced by the Aspergillus fungus and can lead to malignancies or illnesses of the kidney, liver, spleen, stomach, colon, and lungs.
Residents of Florida, Texas, Louisiana, California, and Georgia have been alerted to be on the lookout for Aspergillus fumigatus, and five US states have been listed as being at danger.
Due to hot climates and agricultural activity, scientists have discovered that the fungus is spreading throughout the United States, with the aforementioned states experiencing the worst of it.
The risk of heavily populated places with ageing infrastructure is an additional concern for hub cities such as New York, Houston, and Los Angeles.
Infections, hospitalisations, and fatalities are not being monitored because aspergillosis is not a disease that requires reporting. It is therefore more difficult to identify. Physicians advised patients with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV or cancer, to stay away from mouldy environments, dirt, and gardening. Additionally, they are instructed to endeavour to maintain clean air in homes and hospitals and to wear masks in dusty regions.
Hospitals have stepped up their mould inspections and antifungal procedures in response to Aspergillus fumigatus.
Speaking to the Financial Times, the University of Manchester’s Norman van Rhijn said, “We’re talking about hundreds of thousands of lives, and continental shifts in species distributions. In 50 years, where things grow and what you get infected by is going to be completely different.”
According to the University of Manchester, Aspergillus fumigatus might increase by 75% by 2100 if fossil fuel consumption continues at its current rate.
Although invasive aspergillosis is less prevalent, it is far more deadly. Approximately 400,000 instances of aspergillosis progress to chronic pulmonary aspergillosis, a long-term lung infection. According to one study, just 25% of patients receiving stem cell transplants survived a year after contracting the infection, compared to only 59% of organ transplant recipients. Hospitalisations for invasive aspergillosis increased by 3% per year between 2000 and 2013. Nearly 15,000 hospital stays had been reported by 2014, costing $1.2 billion. Even more concerning is the fact that aspergillosis is one of the top four infections that are most likely to result in mortality according to ICU autopsies. A ‘critical priority’ fungal danger, Aspergillus fumigatus has been designated by the WHO because of its increasing mortality rates and medication resistance.
Now Trending:
- Aspergillus Fungus Threatens Millions As It Spreads Due To Climate Change, Scientists Warn
- Scientists Warn Melting Arctic Ice Could Release Ancient, Potentially Deadly Pathogens
- Scientists Achieve First Dream-To-Dream Communication Using Brain Waves
Please SHARE this story with Family and Friends and let us know what you think about it in the comments!

